Amino acids play a central role in metabolic processes, with their supplementation increasingly recognized for optimizing physiological performance, cognitive function, and disease mitigation. Among these, L-tyrosine, a non-essential but conditionally indispensable amino acid, has emerged as a key functional component in compound amino acid dietary supplements. In this blog post, Viablife, a high purity health food ingredient manufacturer, will share the application of high quality L-tyrosine powder in compound amino acid dietary supplements.
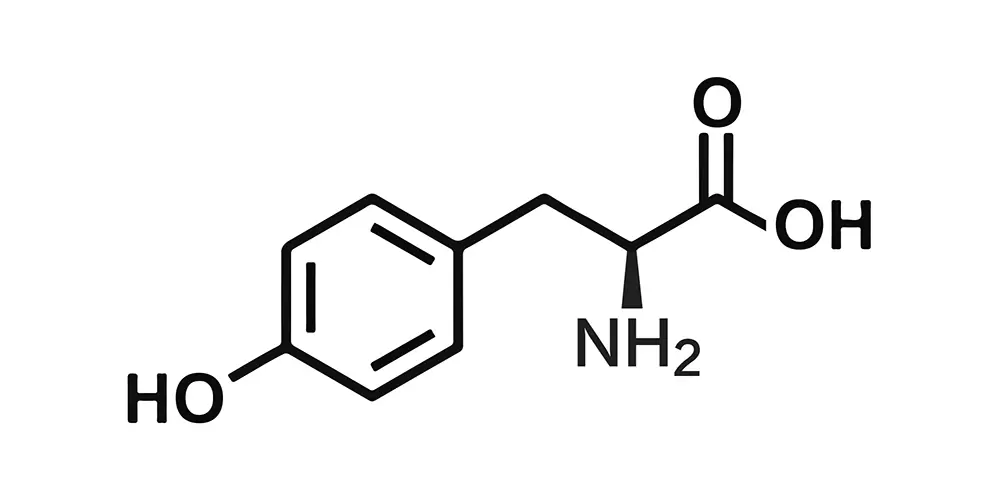
Biochemical Profile of L-tyrosine Powder
L-tyrosine (C₉H₁₁NO₃) is an aromatic amino acid derived primarily from the hydroxylation of phenylalanine via the enzyme phenylalanine hydroxylase (PAH). It is characterized by a phenol side chain, which confers unique biochemical reactivity, including participation in enzymatic and redox reactions. L-tyrosine serves as a precursor for several critical biomolecules:
* Catecholamines: Dopamine, norepinephrine, and epinephrine
* Thyroid hormones: Thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3)
* Melanin: Via enzymatic oxidation by tyrosinase
Given its multifunctionality, L-tyrosine is pivotal in neurotransmission, metabolic regulation, and stress adaptation.
Physiological Roles of L-tyrosine Powder
1. Neurotransmitter Synthesis and Cognitive Performance
L-tyrosine acts as a precursor in the synthesis of dopamine and norepinephrine, which are essential for executive function, mood regulation, and alertness. Under stress, cognitive resources are strained due to increased catecholamine turnover. Tyrosine supplementation can restore neurotransmitter balance, enhancing working memory, task performance, and resilience to stress-induced cognitive decline.
2. Thyroid Function and Metabolic Regulation
The incorporation of L-tyrosine in the synthesis of T3 and T4 is indispensable for basal metabolic rate control. Deficiency in either iodine or tyrosine can impair thyroid hormone production. Supplementation in compound form ensures optimal levels of these hormones, particularly in scenarios involving metabolic syndromes, hypothyroidism, or chronic fatigue.
3. Melanin Production and Photoprotection
Through enzymatic action, L-tyrosine contributes to melanin biosynthesis in melanocytes. Though less commonly highlighted in supplements, this pathway has implications for dermatological health and photoprotection, especially in formulations targeting skin health.

Applications of L-tyrosine Powder in Compound Supplements
Compound amino acid formulations are designed to achieve synergistic metabolic support by combining essential and conditionally essential amino acids. L-tyrosine's integration into such formulations is governed by several strategic considerations:
1. Cognitive and Stress Formulations
L-tyrosine is frequently combined with branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs), taurine, and tryptophan in cognitive support supplements. The rationale lies in balancing excitatory and inhibitory neurotransmission:
* BCAAs reduce central fatigue by modulating serotonin pathways.
* Tryptophan and tyrosine together ensure serotonin and catecholamine balance.
* Taurine acts as a GABAergic modulator, enhancing tyrosine’s effect on focus and calmness.
These combinations are particularly relevant in nootropic stacks targeting students, professionals, military personnel, or individuals exposed to high cognitive load environments.
2. Sports Nutrition and Physical Performance
In sports and endurance formulations, L-tyrosine contributes to the delay of central fatigue and preservation of mental acuity under physical stress. When co-administered with BCAAs, arginine, and carnitine, tyrosine helps maintain neurotransmitter equilibrium during extended periods of physical exertion. This synergy is critical in avoiding performance drops associated with overtraining or prolonged aerobic activity.
3. Thyroid Support Complexes
L-tyrosine is a standard component in supplements aimed at thyroid support, often alongside selenium, iodine, and zinc. These micronutrients support various stages of thyroid hormone synthesis and activation. By ensuring an abundant supply of tyrosine, these formulations support euthyroid status in at-risk populations such as individuals with autoimmune thyroiditis or subclinical hypothyroidism.
4. Mood and Mental Health Supplements
In combination with SAMe (S-adenosylmethionine), 5-HTP, and vitamin B6, L-tyrosine contributes to mood stabilization by influencing dopaminergic and noradrenergic systems. Such formulas are increasingly used in alternative or adjunctive therapies for depression, anxiety, and attention deficit disorders.
Conclusion
L-tyrosine stands as a versatile and potent contributor to compound amino acid dietary supplements. Its biochemical roles in neurotransmitter synthesis, thyroid function, and melanin production make it an invaluable tool in formulating supplements for cognitive performance, stress resilience, metabolic support, and mood regulation. As formulation science evolves, the integration of L-tyrosine with synergistic compounds and novel delivery systems promises to unlock new frontiers in personalized nutrition and supplementation.
References
1.Jongkees, B. J., et al. (2015). The influence of tyrosine supplementation on cognitive performance: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews, 38, 110-122.
2.Deijen, J. B., et al. (1999). Tyrosine improves cognitive performance and reduces blood pressure in cadets after one week of a combat training course. Brain Research Bulletin, 48(2), 203-209.
3.Fernstrom, J. D., & Fernstrom, M. H. (2007). Tyrosine, phenylalanine, and catecholamine synthesis and function in the brain. The Journal of Nutrition, 137(6), 1539S–1547S.
4.Lieberman, H. R. (2003). Nutrition, brain function and cognitive performance. Appetite, 40(3), 245-254.
5.Wurtman, R. J., et al. (1980). The effects of nutrient precursors on the synthesis of brain neurotransmitters. Science, 207(4427), 405–412.





 Leave a Message
Leave a Message