Building on the previous discussion about Nicotinamide' s antioxidant benefits, this article focuses on the following key findings: Studies have demonstrated that Nicotinamide is an effective antioxidant. It protects keratinocytes by reducing the NADP/NADPH ratio, thereby inhibiting the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS).
Nicotinamide (nicatinamide, vitamin B3) is recognized as a potent antioxidant ingredient in cosmetics. Scientific evidence confirms that Nicotinamide regulates oxidative balance by lowering the NADP/NADPH ratio, thereby inhibiting excessive reactive oxygen species (ROS) formation. This redox regulation helps protect skin cells from oxidative stress, one of the key causes of aging, inflammation, and barrier damage.
As a multifunctional active, Nicotinamide not only scavenges free radicals but also prevents oxidative reactions that damage lipids, proteins, and DNA. These protective effects make it an essential component in skincare formulations designed for environmental defense.
Antioxidant Mechanism of Nicotinamide
The antioxidant mechanism of Nicotinamide involves multiple enzymatic pathways that control ROS production. Nicotinamide inhibits NADPH oxidase and xanthine oxidase, reducing the formation of superoxide anions and hydrogen peroxide. It also enhances the activity of superoxide dismutase (SOD) and catalase, enzymes that convert reactive intermediates into harmless molecules like water and oxygen.
In addition, Nicotinamide modulates nitric oxide synthase (NOS) activity, lowering the generation of nitric oxide and peroxynitrite. This dual mechanism—reducing ROS production and enhancing ROS elimination—stabilizes the cellular redox environment and helps maintain mitochondrial and epidermal health.
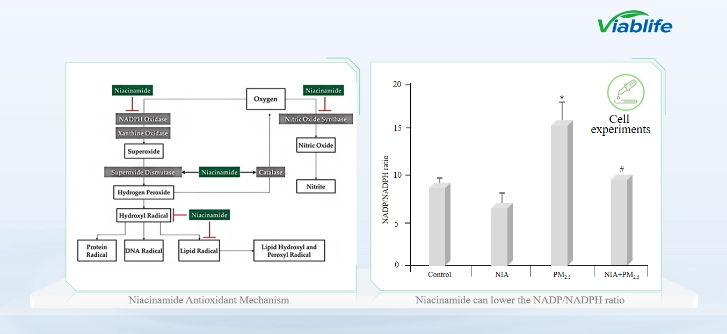
Regulation of the NADP/NADPH Ratio
The NADP/NADPH ratio is a crucial indicator of oxidative stress. Under harmful environmental exposure such as PM2.5 particles, this ratio increases, signaling higher oxidative activity. In vitro studies show that Nicotinamide can significantly decrease the NADP/NADPH ratio, restoring redox balance in skin cells.
This biochemical effect enhances the cell' s ability to recycle NADPH, supporting continuous antioxidant enzyme activity. As a result, Nicotinamide improves the resilience of skin cells under oxidative stress conditions, contributing to long-term protection and recovery.
Protection Against Molecular Oxidative Damage
Through its redox-regulating capacity, Nicotinamide protects key biomolecules from ROS—induced damage. It limits lipid peroxidation, maintains protein structure and enzymatic activity, and prevents oxidative DNA breaks. These actions are essential for preserving cellular integrity and reducing premature skin aging.
Experimental data demonstrate that skin cells treated with Nicotinamide exhibit lower oxidative injury compared to untreated controls when exposed to pollutants. This confirms Nicotinamide' s efficiency as a functional antioxidant in cosmetic applications.
Scientific Implications for Cosmetic Formulation
For skincare researchers and formulators, the antioxidant activity of Nicotinamide provides a clear biochemical foundation for product development. By optimizing Nicotinamide concentration and combining it with complementary antioxidants such as vitamins C or E, formulators can enhance product stability and antioxidant performance.
Furthermore, the NADP/NADPH ratio can serve as a measurable endpoint in antioxidant efficacy testing, enabling evidence-based cosmetic claims.
Conclusion
Nicotinamide is a scientifically validated antioxidant active that regulates ROS generation and sustains redox equilibrium by modulating the NADP/NADPH balance. It effectively protects lipids, proteins, and DNA from oxidative stress, making it a cornerstone molecule in modern skincare formulations aimed at pollution defense and cellular.
Data Source:
Mechanistic Insights into the Multiple Functions of Nicotinamide: Therapeutic Implications and Cosmeceutical Applications in Functional Skincare Products
Zhen A X , Mei J P , Kang K A , et al. Nicotinamide Protects Skin Cells from Oxidative Stress Induced by Particulate Matter[J]. Biomolecules, Therapeutics, 2019, 27(6).





 Leave a Message
Leave a Message