Nicotinamide, also known as niacinamide (CAS No.:98-92-0), has become one of the most respected skincare ingredients due to its multifunctional benefits for improving skin tone, reducing inflammation, and supporting the skin' s barrier. In this blog post, Viablife will share the reasons why skin darkens and how the continuous use of nicotinamide can significantly brighten skin tone. Nicotinamide has become a core ingredient in modern skin whitening formulations.
How Does The Skin Ture Black
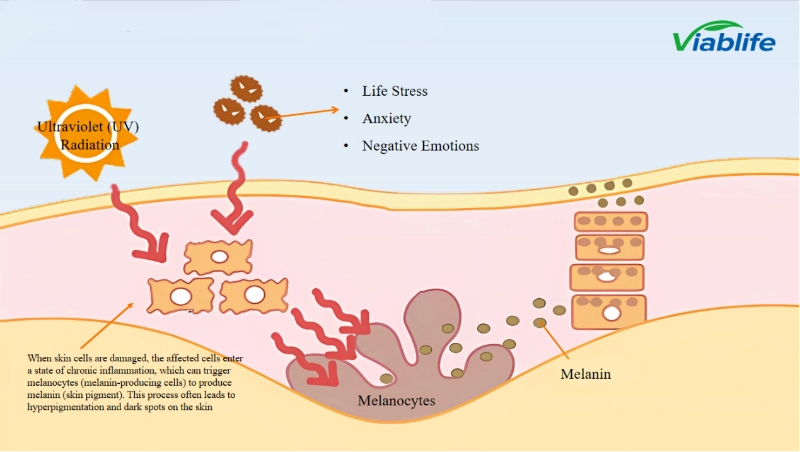
How Nicotinamide' s Skin Benefits Support Brightening Mechanisms
To understand why nicotinamide is effective in brightening skincare, it is first important to understand how skin becomes darker in the first place. Factors such as ultraviolet (UV) radiation, life stress, anxiety, and negative emotions can stimulate a cascade of inflammatory responses in the skin. When skin cells are damaged, this chronic inflammation signals melanocytes to produce more melanin, the pigment responsible for dark spots, uneven tone, and hyperpigmentation.
Nicotinamide' s benefits for skin begin at the cellular level, where it helps interrupt this cycle. As a form of vitamin B3, it supports healthier cell function, stabilizes skin against external stress, and reduces the mechanisms that trigger excessive melanin production.
Nicotinamide in Cosmetics Brightening the Skin Through Multiple Pathways
In 1974, researchers found that nicotinamide had the ability to absorb UV radiation, an essential factor in preventing UV-induced pigmentation. More importantly, they determined that combining 1-5% nicotinamide with 1-4% sunscreen agents resulted in effective whitening and photoprotection.
This dual function—UV absorption and pigment suppression—set the stage for nicotinamide to be widely adopted in skincare products aimed at brightening, spot reduction, and overall complexion improvement.
A key mechanism behind nicotinamide brightening lies in its ability to:
* Inhibit melanosome transfer: Nicotinamide prevents melanin-filled melanosomes from transferring from melanocytes to surrounding skin cells. This means less pigment reaches the upper layers of skin.
* Reduce inflammation: Since inflammation can directly stimulate pigment production, nicotinamide' s anti-inflammatory nature helps calm skin and prevent over-pigmentation.
* Improve skin barrier function: A stronger barrier reduces irritation and environmental stress, leading to a more even complexion over time.
Clinical Evidence Supporting Nicotinamide Benefits for Skin Brightening
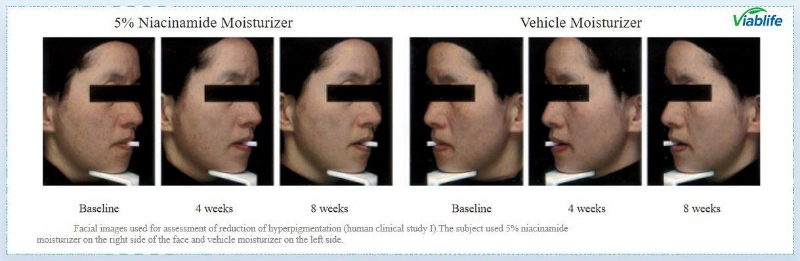
In comparative studies, participants applied 5% nicotinamide moisturizer on one side of the face and a placebo (vehicle moisturizer) on the other. Over 4 and 8 weeks, the side treated with nicotinamide showed a noticeable improvement in hyperpigmentation, brightness, and texture.
This demonstrates that:
• Nicotinamide brightening effects are gradual but consistent.
• Visible improvements emerge around 4 weeks.
• Results become more pronounced by 8 weeks.
• Nicotinamide is well tolerated even by sensitive skin.
These results align with additional research conducted in 2002 by Procter & Gamble in partnership with the University of Cincinnati, confirming nicotinamide' s efficacy in reducing age spots and improving uneven tone.
Role of Nicotinamide Benefits for Skin in Preventing Hyperpigmentation
UV rays penetrate the upper layers of skin and activate melanocytes in the basal layer. When these cells detect oxidative stress or inflammation, they accelerate melanin production as a protective mechanism. Over time, this leads to dark patches or spots, especially in individuals exposed to sun, pollution, or emotional stress.
By addressing both the cause and the result, nicotinamide benefits for skin provide a comprehensive defense against hyperpigmentation. It:
• Reduces oxidative stress that triggers pigment formation.
• Helps regulate melanin synthesis.
• Improves cellular repair mechanisms.
• Strengthens the epidermal barrier, reducing sensitivity.
These biological advantages make nicotinamide effective in preventing the development of new dark spots while improving the appearance of existing ones.
Conclusion
From the biological processes that cause skin darkening to the clinical proof supporting nicotinamide, it is clear that nicotinamide benefits for skin extend far beyond simple moisturization. It reduces inflammation, moderates melanin transfer, supports barrier repair, and provides UV-related protection—making it a comprehensive brightening ingredient suitable for all skin types.
Data Source:
The effect of niacinamide on reducing cutaneous pigmentation and suppression of melanosome transfer[J]. British Journal of Dermatology, 2002, 147(1):20-31.





 Leave a Message
Leave a Message