Skin redness is commonly associated with epidermal barrier damage and irritation-induced inflammatory responses. To objectively evaluate the soothing effect of Viablife Ceramide on redness-related skin conditions, its performance was assessed through a combination of in vitro epidermal model testing and human clinical evaluation. The results establish a clear link between epidermal repair, inflammatory regulation, and visible redness improvement.
Soothing Effect Evaluation Based on 3D Epidermal Skin Model(EpiKutis)
To investigate the biological response of irritated skin, a 3D epidermal skin model (EpiKutis) was used. This model simulates the structural and functional features of human epidermis and allows direct observation of tissue morphology and biochemical changes following chemical stimulation.
SLS-Induced Epidermal Damage and Experimental Design
Sodium lauryl sulfate (SLS) was applied to induce epidermal damage, mimicking irritation-related conditions that commonly lead to skin redness. The study included the following groups:
• Blank Control group (BC): normal epidermal tissue without treatment
• Negative Control group (NC): epidermal tissue exposed to SLS
• Experimental group (C2): SLS-exposed tissue treated with 1.0% Viablife Ceramide 50
This design enabled direct comparison between intact skin, damaged skin, and skin after ceramide intervention.
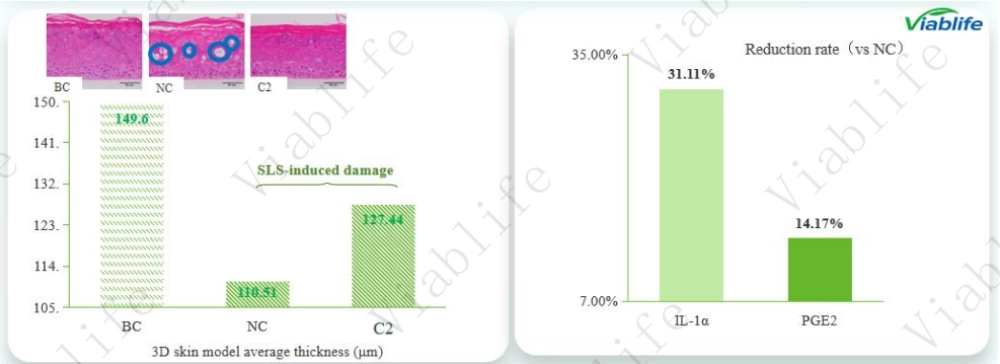
Epidermal Morphology and Thickness Recovery
Average epidermal thickness was used as a key indicator of tissue integrity. SLS exposure led to a pronounced reduction in epidermal thickness, reflecting structural damage.
Measured average thickness values were:
• Blank Control: approximately 149.6 μm
• SLS-induced damage group: approximately 106.3 μm
• Viablife Ceramide-treated group: approximately 125.9 μm
Compared with the negative control, the ceramide-treated group showed a clear recovery in epidermal thickness. Histological images further confirmed improved tissue organization and reduced damage severity, indicating that Viablife Ceramide contributed to restoring epidermal structure after irritation.
Reduction of Inflammation-Related Factors
In addition to structural changes, the soothing effect was evaluated by measuring inflammatory mediators associated with redness development:
• Interleukin-1α (IL-1α)
• Prostaglandin E2 (PGE2)
Compared with the SLS-damaged group, treatment with Viablife Ceramide led to significant measurable reductions:
• IL-1α reduction rate: 31.11%
• PGE2 reduction rate: 14.17%
These findings suggest that Viablife Ceramide helped moderate inflammation-related signaling induced by SLS, supporting its soothing effect at the cellular level.
Human Clinical Trial on Redness and Skin Sensitivity
To confirm whether the in vitro results translate into visible and sensory improvements, a human clinical trial was conducted using a formulation containing Viablife Ceramide.
Clinical Study Design
• Number of subjects: 17 volunteers
• Test product: lotion containing 1.0% Viablife Ceramide 50
• Duration: 4 weeks of continuous application
• Evaluation parameters:
• Proportion of redness area on the cheeks
• Lactic acid stinging score in the nasolabial folds
• Evaluation tools: VISIA 7 imaging system and standardized stinging assessment
This design enabled both objective image-based analysis and assessment of skin sensitivity.
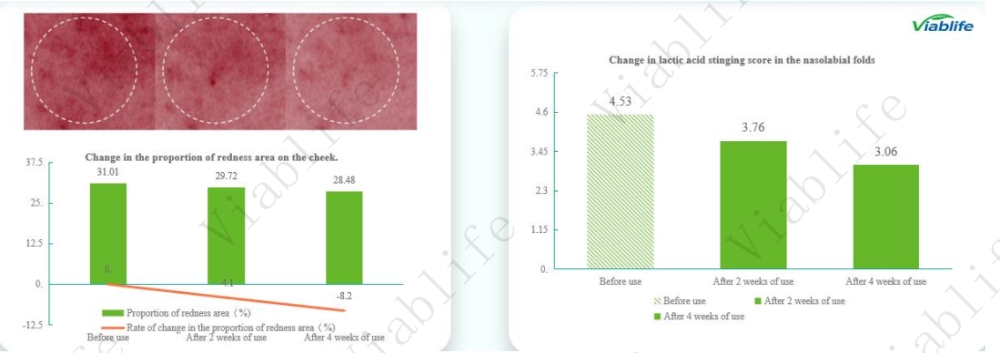
Changes in Facial Redness Area
Cheek redness was quantified by calculating the proportion of the redness area. The results showed a continuous downward trend during the study period:
• Before use: 31.01%
• After 2 weeks of use: 29.72%
• After 4 weeks of use: 28.48%
After four weeks, cheek redness decreased by 8.15%, indicating a gradual improvement associated with continued use of the ceramide-containing formulation.
Improvement in Lactic Acid Stinging Response
Skin sensitivity was evaluated using a lactic acid stinging test in the nasolabial folds. Average stinging scores decreased progressively over time:
• Before use: 4.53
• After 2 weeks of use: 3.76
• After 4 weeks of use: 3.06
The reduction in stinging scores reflects improved skin tolerance to chemical stimulation, consistent with the soothing effect observed in the epidermal model.
Overall Interpretation of Soothing Effect
When considered together, the results from the 3D epidermal skin model and the human clinical trial demonstrate a consistent pattern:
• Viablife Ceramide supports recovery of epidermal structure after chemical irritation
• Inflammation-related mediators associated with redness are reduced
• Visible facial redness decreases with continued use
• Skin sensitivity, measured by stinging response, is alleviated
This alignment between laboratory findings and human outcomes indicates that the soothing effect of Viablife Ceramide is supported by both biological and clinical evidence.
Viablife Ceramide – Redefine Ceramide Formulation
Viablife Ceramide is designed to overcome key formulation challenges associated with conventional ceramides. The ingredient can be dispersed in water at room temperature, eliminating reliance on high-temperature processing and improving formulation flexibility. It maintains excellent stability across high-temperature, low-temperature, and thermal cycling conditions, ensuring consistent performance in diverse formulation environments. By simplifying the system and reducing unnecessary components, Viablife Ceramide helps minimize the risk of ineffective additions and formulation instability. In addition, with 50% Viablife Ceramide NP content, the ingredient guarantees reliable active delivery, providing formulators with both technical confidence and measurable efficacy.
Conclusion
Through evaluation using a 3D epidermal skin model and a controlled human clinical trial, Viablife Ceramide exhibits a measurable ability to alleviate skin redness. The ingredient contributed to epidermal structural recovery, reduction of inflammation-related markers, and improvement in visible redness and stinging sensation. These results provide data-supported evidence for its application in formulations targeting redness-prone and irritation-sensitive skin.




 Leave a Message
Leave a Message